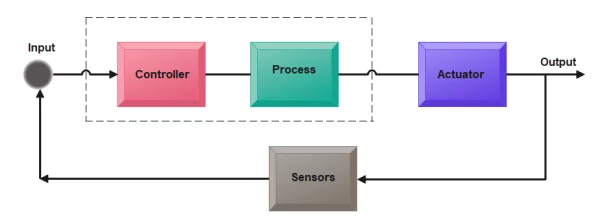
Feedback Control System
A feedback control system is a control system that uses measurements of the output of a system to adjust the input in order to achieve a desired output. The system continuously monitors the output and compares it to a setpoint or reference value, and then adjusts the input to minimize the difference between the actual and desired output.
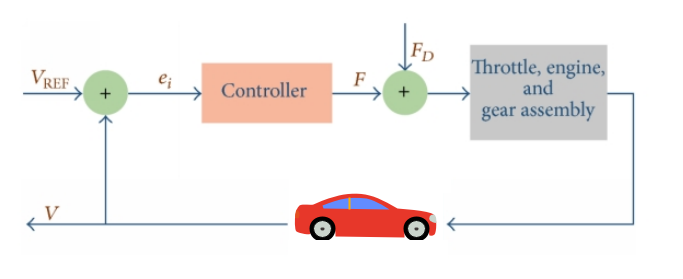
Examples
A cruise control system in an automobile is an example of a feedback control system. The driver sets the desired speed of the car, and the system continuously monitors the speed and adjusts the throttle to maintain the specified speed. If the automobile is moving too slowly, the system increases the throttle; if it is moving too quickly, the system decreases the throttle. The system uses the speedometer as feedback to adjust the throttle and maintain the desired speed.
A thermostat in a heating system is another example of a feedback control system. The thermostat measures the temperature of a room and compares it to the user-specified temperature. If the temperature is too low, the thermostat activates the heating system to raise it, and if the temperature is too high, the thermostat deactivates the heating system to lower it.
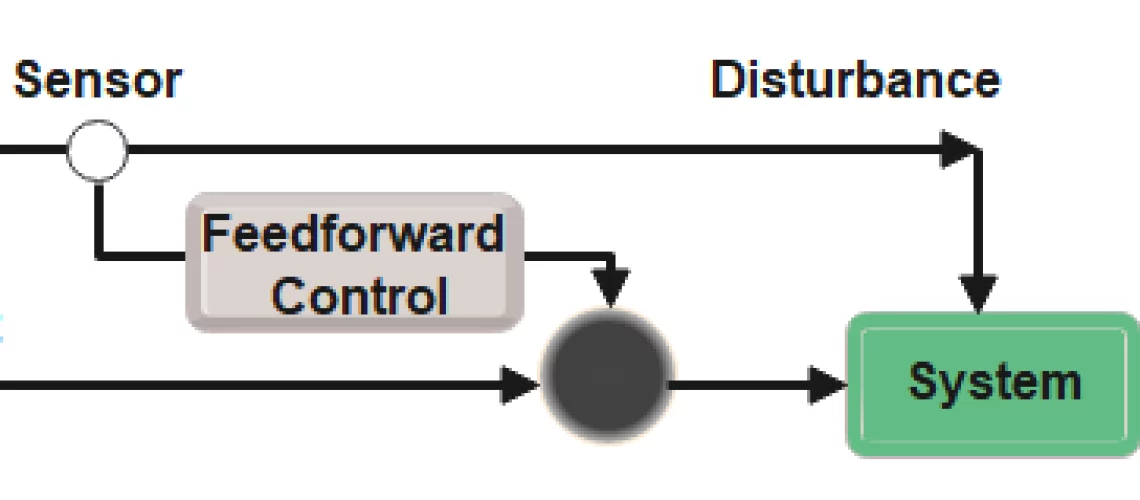
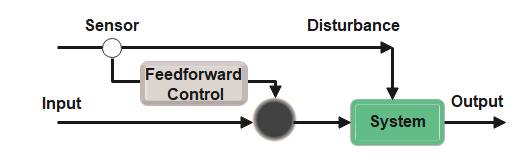
Feedforward Control System
A feedforward control system is a control system that uses measurements of disturbances or inputs to the system to predict the output and adjust the input accordingly. In this type of control system, the input is adjusted before the disturbance affects the output, which can result in faster and more accurate control.
Examples
An example of a feedforward control system is an aircraft control system. The aircraft control system continuously measures the aircraft’s altitude, velocity, and attitude, and predicts the effects of external disturbances such as wind gusts or turbulence. Based on these predictions, the control system adjusts the position of control surfaces such as flaps or ailerons to maintain stability and control of the aircraft. The system uses the measurements of disturbances and inputs to predict the output and adjust the control surfaces before the disturbance affects the aircraft’s behaviour.
Another example of a feedforward control system is a robotic arm in a manufacturing process. The robotic arm measures the position and orientation of a workpiece and predicts the effects of disturbances such as changes in the workpiece’s position or weight.
Cascade Control System
A cascade control system is a control system that combines both feedback and feedforward control strategies. It consists of two or more control loops, with the output of the first loop serving as the setpoint for the second loop. The first loop controls a process variable, while the second loop controls a related variable that affects the first variable.
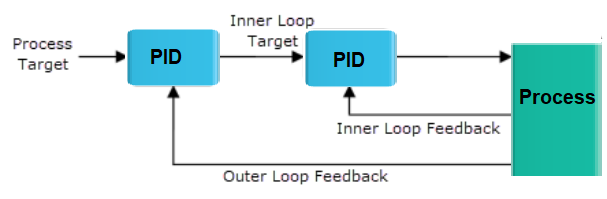
Examples
An example of a cascade control system is a temperature control system in a chemical reactor. The primary loop controls the temperature of the reactor by adjusting the heating or cooling system and uses feedback control to maintain the desired temperature. However, changes in the flow rate of the reactants or cooling fluid can affect the temperature of the reactor, which can cause disturbances in the primary loop. To address this issue, a secondary loop can be added to control the flow rate of the cooling fluid. The output of the primary loop, which is the temperature of the reactor, serves as the setpoint for the secondary loop. The secondary loop uses feedforward control to predict the effect of changes in the flow rate of the cooling fluid on the temperature of the reactor and adjusts the flow rate to maintain the desired temperature.
References:
- https://www.britannica.com
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- https://www.sciencedirect.com