In petroleum refining, acid gas refers to a mixture of gases that form acids in a solution with water. The most common types of acid gas are carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S), though there are some other acidic gases including hydrogen chloride (HCI), hydrogen fluoride (HF), sulphur oxides (SO2 and SO3) and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
The acid gas removal process is important because the H2S and CO2 can be corrosive and toxic, and they can also interfere with the processing of the other products in the refinery. Further, its presence in refinery streams will reduce the purity of Hydrogen in Hydrogen consuming plants of the refinery and cause damaging impacts on the catalysts.
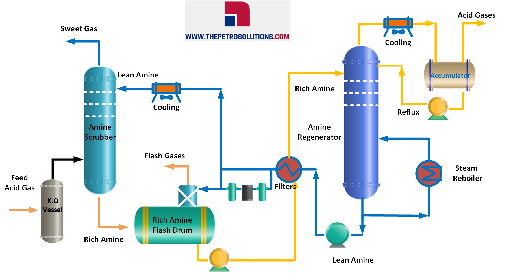
The acid gas is typically removed from the gas stream using a process called acid gas treatment, which involves the use of specialized equipment such as amine or physical solvent absorbers. Treating with alkanolamines removes acid gases (H2S and CO2 ) from fuel gas and various refinery off-gas streams. In refineries, H2S-laden Amine (Rich Amine) goes to the sulfur recovery unit. There, the H2S is stripped off with steam, and the amine is recirculated. The H2S is converted into elemental sulfur in a Claus Sulfur Recovery Unit.
Once the acid gas is removed, it is often processed further to recover the valuable sulfur content, which can be used in a variety of industrial applications. The recovered sulfur can be used to produce fertilizers, chemicals, and other products.
Sources of Acid and Sour Gases in an Oil Refinery
Sources of acid or sour gases depend upon the refinery configuration and processing units. Refineries processing heavy crude oils have higher quantities of sour and acid gases. Some of the major sources of acid gases in petroleum refineries are as follows;
- Gases removed from the crude distillation columns contain a sufficient amount of H2S.
- Sulfur compounds present in naphtha, diesel, and Vacuum Gas oil are converted to H2S in hydrotreating reactors. Hydrotreating recycle gas streams and stripper off-gas streams are highly rich in H2S.
- Refinery fuel gases are produced in crude distillation columns and other refinery streams and are also treated by Amine Scrubbing to prevent corrosion problems and increase the heating value of the gas.
- Liquefied petroleum gas separated from refinery gas streams.
- CO2 from synthesis gas at hydrogen production plants.
- Removal of H2S/CO2 from the natural gas streams.
- Sour water produced in various refinery operations (Hydrotreating, Hydrocracking units) also contains a significant quantity of sour gases. Acid gases produced from Sour Water Treatment are called Foul Acid Gases while from amine treating of other refinery streams are called Clean Acid Gases.
Acid Gasses Vs Sour Gases
Sour Gas contains only hydrogen sulfide while acid gas is a broad term that contains all types of acidic gases including carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, HCl, HF and NOXs, etc.
References
- Springer Handbook of Petroleum Technology, Hsu Robinson Editors
- Amine Gas Treating Process
- Types of Alkanolamines for Acid Gas Treatment
- www.envirotech-online.com
Certified Functional Safety Professional (FSP, TÜV SÜD), Certified HAZOP & PHA Leader, LOPA Practitioner, and Specialist in SIL Verification & Functional Safety Lifecycle, with 18 years of professional experience in Plant Operations and Process Safety across Petroleum Refining and Fertilizer Complexes.
- Nasir Hussainhttps://thepetrosolutions.com/author/admin/
- Nasir Hussainhttps://thepetrosolutions.com/author/admin/
- Nasir Hussainhttps://thepetrosolutions.com/author/admin/
- Nasir Hussainhttps://thepetrosolutions.com/author/admin/






